23405.A block (B) is attached to two unstretched springs S1 and S2 with spring constants k and 4k, respectively (see figure I). The other ends are attached to identical supports M1 and M2 not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block B is displaced towards wall 1 by a small distance $x$ (figure II) and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2. Displacements $x$ and y are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block B. The ratio y/x is
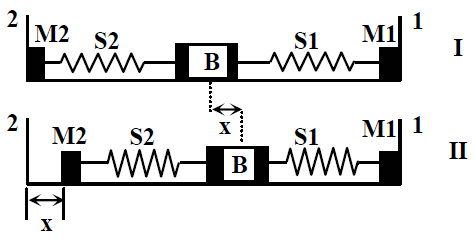

4
2
1/2
1/4
23406.Two identical balls A and B having velocities of 0.5 m/s and –0.3 m/s respectively collide elastically in one dimension. The velocities of B and A after the collision respectively will be
–0.5 m/s and 0.3 m/s
0.5 m/s and –0.3 m/s
–0.3 m/s and 0.5 m/s
0.3 m/s and 0.5 m/s
23407.This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
If two springs S1 and S2 of force constants k1 and k2, respectively, are stretched by the same force, it is found that more work is done on spring S1 than on spring S2.
Statement 1 : If stretched by the same amount, work done on S1, will be more than that on S2
Statement 2 : k1 < k2
If two springs S1 and S2 of force constants k1 and k2, respectively, are stretched by the same force, it is found that more work is done on spring S1 than on spring S2.
Statement 1 : If stretched by the same amount, work done on S1, will be more than that on S2
Statement 2 : k1 < k2
Statement 1 is false, Statement 2 is true.
Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is true, Statement 2 is the correct explanation for statement 1.
Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is true, Statement 2 is not the correct explanation of Statement 1.
23408.A particle of mass m moving in the $x$ direction with speed 2v is hit by another particle of mass 2m moving in the $y$ direction with speed v. If the collision is perfectly inelastic, the percentage loss in the energy during the collision is close to
44%
50%
56%
62%
23409.A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up? Fat supplies 3.8 × 107 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g = 9.8 ms–2
6.45 × 10–3 kg
9.89 × 10–3 kg
12.89 × 10–3 kg
2.45 × 10–3 kg
23410.A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power k watts. If the particle starts from rest the force on the particle at time t is
$\sqrt{\dfrac{mk}{2}} t^{–\dfrac{1}{2}}$
$\sqrt{mk} t^{–\dfrac{1}{2}}$
$\sqrt{2mk} t^{–\dfrac{1}{2}}$
$\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{mk} t^{–\dfrac{1}{2}}$
23411.Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ such that KP > KQ. They are stretched first by the same amount (case a), then by the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as, in case (a) and case (b), respectively
WP = WQ ; WP > WQ
WP = WQ ; WP = WQ
WP > WQ ; WQ > WP
WP < WQ ; WQ < WP
23412.A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms–1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is
1.00 J
0.67 J
0.34 J
0.16 J
23413.Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are v and 2v respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at A, these two particles will again reach the point A?
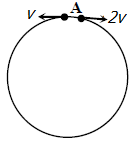

4
3
2
1
23414.A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x–axis. It is at rest and from t = 0 onwards it is subjected to a time–dependent force F(t) in the $x$ direction. The fore F(t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is 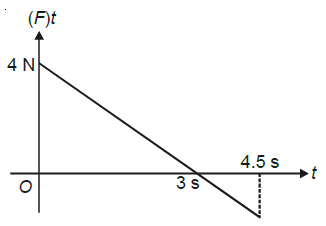

4.50 J
7.50 J
5.06 J
14.06 J
