|
Among $CaH_2, BeH_2 , BaH_2,$ the order of ionic character is
|
Answer
|
|
Consider the change in oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below :
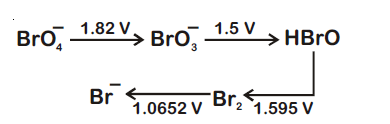
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is
|
Answer
|
|
For the redox reaction
$MnO_4^-+C_2O_4^{2-}+H^+\rightarrow Mn^{2+} +CO_2 + H_2O$
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced equation are
$MnO_4^-$ $C_2O_4^{2-}$ $H^+$
|
Answer
|
|
Which one of the following conditions will favour maximum formation of the product in the reaction,
$A_2(g)+B_2(g)\rightleftharpoons X_2(g)\triangle_r H=-XKJ?$
|
Answer
|
|
When initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of a zero order reaction
|
Answer
|
|
The bond dissociation energies of $X_2 , Y_ 2$ and XY are in the ratio of 1 : 0.5 : 1. ΔH for the formation of XY is –200 kJ $mol^{–1}$. The bond dissociation energy of $X_2$ will be
|
Answer
|
|
The correction factor ‘a’ to the ideal gas equation corresponds to
|
Answer
|
|
Consider the following species :
$CN^+, CN^–, NO$ and CN
Which one of these will have the highest bond order?
|
Answer
|
|
Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is $1s^2 2s^2 2p^3$, the simplest formula for this compound is
|
Answer
|
|
Iron exhibits bcc structure at room temperature. Above 900°C, it transforms to fcc structure. The ratio of density of iron at room temperature to that at 900°C (assuming molar mass and atomic radii of iron remains constant with temperature) is
|
Answer
|