Java DataType
The data stored in the memory of the computer can be of many types.
Data type specifies the size and type of values that can be stored in an identifier.
Different data types allow you to select the type appropriate to the needs of the application.
DataType Types
1) Primitive - which include Integer, Character, Boolean, and Floating Point.
2) Non-primitive - which include Classes, Interfaces, and Arrays.
Primitive DataTypes Chart
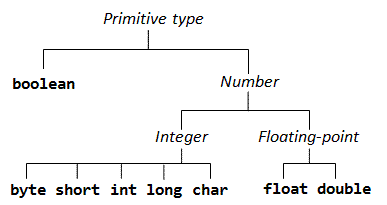
| Type | Size | Value | Example Literals |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 bit | 0 or 1 | true,false |
| byte | 8 bits | -128 to +127 | byte n=100; |
| short | 16 bits | -32768 to + 32767 or -216 to 216-1 |
short m=25000; |
| int | 32 bits | -232 to 232-1 | int a=100000; |
| long | 64 bits | -264 to 264-1 | long var=1000000000; |
| char | 16 bits | '\u0000' to '\uffff' | char c='a'; char x='\u1010'; |
| float | 32 bits | float i = 1.5f float j = -1.23e100f |
|
| double | 64 bits | double x = 0.05d; double y = 1.23456e300d; |
Working with float and double
Syntax for float datatype
float a=10.5f;
Example:Print the value of float variable
public class FloatDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
float fval = 10.0f;
System.out.println("Float Number : " + fval);
}
}
Try it Yourself
Note: String and any number can be printed together using + in between values, as above. To print two strings we can use System.out.println(" Sun "+ "Light" );
Exercise :
Exercise 1: Finding Area of Circle.
double radius, pi, area;
radius = 9.8;
pi = 3.14;
area = pi * radius * radius;
System.out.println("Area of Circle with Radius "+ radius + " is : "+ area);
Do it Yourself
How to print a character in Java?
The char is a keyword which is used to store a single character such as 'a', 'Z', '9', '&', '$' and so on.
Character can be letters, digits or special symbols. Characters are always enclosed in single quotes .
We can also use ASCII code to represent value of character.To see ascii values click here
Syntax
char x = 'A'; char y = 65; // Ascii code for char A is 65.
Example:Print the value of character variable
public class CharDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
char oneChar1 = 'A';
char oneChar2 = 65;
System.out.println(oneChar1);
System.out.println(oneChar2);
}
}
65 is the numeric representation of character 'A' , or its ASCII code.
Try it YourselfType Casting
When destination type is smaller than source type, then we need to explicitly cast it.
This is called as 'Type Casting'. This is also called narrowing conversion and truncation.
Syntax
(target-type) value
Example:Int to Byte Conversion
class IntToByteConversion
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int a = 350;
byte b;
b = (byte) a;
System.out.println("b = " + b );
}
}
Try it Yourself
Example:Data type casting
class DatatypeCasting
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
byte b;
int i = 81;
double d = 323.142;
float f = 72.38f;
char c = 'A';
c = (char) i;
System.out.println("i = " + i + " c = " + c);
i = (int) d;
System.out.println("d = " + d + " i = " + i);
i = (int) f;
System.out.println("f = " + f + " i = " + i);
b = (byte) d;
System.out.println("d = " + d + " b = " + b);
}
}
Try it Yourself
Exercise:
Find the output of the following program
public class asciicodes {
public static void main(String args[]) {
char var1 = 'A';
char var2 = 'a';
System.out.println((int)var1 + " " + (int)var2);
}
}
How to print boolean value in java?
A variable of boolean datatype can have two values: true and false (Boolean literals).
Boolean variables are used to indicate whether a condition is true or not, or to represent two states, such as a light being on or off.
Syntax
boolean a=true;
Example:Print the value of boolean variable
public class Demo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
boolean a = true;
System.out.println(a);
}
}
Try it Yourself
Solve this!!
public class Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
boolean a=true;
boolean b=false;
System.out.println(a+" "+b);
}
}
- Collection
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
- HashSet
- Conditional Statements
- Classes and Objects
- Inheritance
- Packages
- Exception Handling
- Threads
- TreeSet
- LinkedHashSet
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- LinkedHashMap
- HashTable
- Iterator and ListIterator
- String
- Scanner
- Array Small Programs
- Introduction
- Variables
- DataTypes
- Operators
- Conditional Statements
- Loop
- Arrays
- Object Oriented Programming
- Classes and Objects
- Access Modifiers
- Methods
- Abstraction
- Constructor
- Packages
- StringBuffer
- Inheritance
- StringBuilder
- Encapsulation
- Java IO
- Polymorphism
- Interface
- Types Of Variables
- Static Keyword
- Final Keyword
- Super Keyword
- This Keyword
- Exception Handling
